Terraform Integration Overview with PGVecto.rs Cloud
This guide walks you through the process of installing and configuring the PGVetco.rs Cloud provider.
1. Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
Terraform Installed: Download and install Terraform from here by following the provided instructions.
PGVecto.rs Cloud Account: Access to PGVecto.rs Cloud and your API Key are essential. Go to the PGVecto.rs Cloud Console and create an API key. The API key must have the
ProjectOwnerpermissions. For more information, see API Key.
2. Download PGVecto.rs Cloud Terraform Provider
Start by configuring the PGVecto.rs Cloud provider within your Terraform configuration file (main.tf). Follow these steps:
terraform {
required_providers {
pgvecto-rs-cloud = {
source = "tensorchord/pgvecto-rs-cloud"
}
}
}3. Initialize Terraform Configuration
Initialize the Terraform configuration by running:
$ terraform init
Initializing the backend...
Initializing provider plugins...
- Reusing previous version of tensorchord/pgvecto-rs-cloud from the dependency lock file
- Using previously-installed tensorchord/pgvecto-rs-cloud v0.0.2
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.Terraform will download the pgvecto-rs-cloud provider and install it in a hidden subdirectory of your current working directory, named .terraform.
4. Authenticate PGVecto.rs Cloud Terraform Provider
Your PGVecto.rs Cloud API Key is required to use the Terraform Provider. There are two ways to configure this.
Option 1: Specify API Key in Provider Block
Append the following code to your main.tf file:
provider "pgvecto-rs-cloud" {
api_key = "<your-api-key>"
}Replace <your-api-key> with your PGVecto.rs Cloud API Key.
Option 2: Use Environment Variable
Set the API key as an environment variable:
export PGVECTORS_CLOUD_API_KEY="<your-api-key>"Then the provider declaration in your main.tf file is simply:
provider "pgvecto-rs-cloud" {
}By following these steps, you should have the PGVecto.rs Cloud Terraform provider configured and ready to move on to the next steps.
4. Manage PGVecto.rs Cloud Cluster
Create a Enterprise Plan
The following example demonstrates how to create a PostgreSQL cluster with the Enterprise plan. For more information about the options, refer to the Resource Schema.
resource "pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster" "enterprise_plan_cluster" {
account_id = "8364ded2-5580-45c4-a394-edfa582e35a0"
cluster_name = "enterprise-plan-cluster"
plan = "Enterprise"
image = "15-v0.3.0-public"
server_resource = "aws-m7i-large-2c-8g"
region = "eu-west-1"
cluster_provider = "aws"
database_name = "test"
pg_data_disk_size = "10"
}
output "psql_endpoint_enterprise" {
description = "Endpoint for the PGVecto.rs Cloud Enterprise PostgreSQL database"
value = pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster.connect_endpoint
}$ terraform validate && terraform plan && terraform output
Success! The configuration is valid.
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are
indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster will be created
+ resource "pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster" "enterprise_plan_cluster" {
+ account_id = "8364ded2-5580-45c4-a394-edfa582e35a0"
+ cluster_name = "enterprise-plan-cluster"
+ cluster_provider = "aws"
+ connect_endpoint = (known after apply)
+ database_name = "test"
+ first_recoverability_point = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ image = "15-v0.3.0-public"
+ last_archived_wal_time = (known after apply)
+ last_updated = (known after apply)
+ pg_data_disk_size = "10"
+ plan = "Enterprise"
+ region = "eu-west-1"
+ server_resource = "aws-m7i-large-2c-8g"
+ status = (known after apply)
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Changes to Outputs:
+ psql_endpoint_enterprise = (known after apply)
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
Note: You didn't use the -out option to save this plan, so Terraform can't guarantee to take exactly
these actions if you run "terraform apply" now.
╷
│ Warning: No outputs found
│
│ The state file either has no outputs defined, or all the defined outputs are empty. Please define an
│ output in your configuration with the `output` keyword and run `terraform refresh` for it to become
│ available. If you are using interpolation, please verify the interpolated value is not empty. You can
│ use the `terraform console` command to assist.$ terraform apply
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are
indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster will be created
+ resource "pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster" "enterprise_plan_cluster" {
+ account_id = "8364ded2-5580-45c4-a394-edfa582e35a0"
+ cluster_name = "enterprise-plan-cluster"
+ cluster_provider = "aws"
+ connect_endpoint = (known after apply)
+ database_name = "test"
+ first_recoverability_point = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ image = "15-v0.3.0-public"
+ last_archived_wal_time = (known after apply)
+ last_updated = (known after apply)
+ pg_data_disk_size = "10"
+ plan = "Enterprise"
+ region = "eu-west-1"
+ server_resource = "aws-m7i-large-2c-8g"
+ status = (known after apply)
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Changes to Outputs:
+ psql_endpoint_enterprise = (known after apply)
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Creating...
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Still creating... [10s elapsed]
...[snip]...
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Still creating... [2m0s elapsed]
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Creation complete after 2m9s [id=9986cfff-9758-4cbc-9433-084fe6e7936f]
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
psql_endpoint_enterprise = "postgres://test_user:plvpx1YvXmBu@enterprise-plan-cluster-hp2goemtvtd5q0ew.eu-west-1-dev.aws.pgvecto.rs:5432/test?sslmode=require"Connect to the cluster
$ psql "postgres://test_user:plvpx1YvXmBu@enterprise-plan-cluster-hp2goemtvtd5q0ew.eu-west-1-dev.aws.pgvecto.rs:5432/test?sslmode=require"
psql (15.3, server 15.8 (Debian 15.8-1.pgdg120+1))
SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, compression: off)
Type "help" for help.
test=> \dx
List of installed extensions
Name | Version | Schema | Description
---------+---------+------------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
pgaudit | 1.7 | public | provides auditing functionality
plpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language
vectors | 0.3.0 | public | vectors: Vector database plugin for Postgres, written in Rust, specifically designed for LLM
(3 rows)
test=> CREATE TABLE test (id integer PRIMARY KEY, embedding vector(3) NOT NULL);
CREATE TABLE
test=> INSERT INTO test SELECT i, ARRAY[random(), random(), random()]::real[] FROM generate_series(1, 100) i;
INSERT 0 100
test=> CREATE INDEX ON test USING vectors (embedding vector_l2_ops) WITH (options = "[indexing.hnsw]");
CREATE INDEX
test=> SELECT * FROM test ORDER BY embedding <-> '[0.40671515, 0.24202824, 0.37059402]' LIMIT 10;
id | embedding
----+---------------------------------------
10 | [0.3603687, 0.2597973, 0.48529512]
68 | [0.341106, 0.36290976, 0.4206507]
46 | [0.29137495, 0.10839028, 0.2966823]
56 | [0.5840259, 0.3336522, 0.33045283]
54 | [0.2123173, 0.21955383, 0.2764878]
97 | [0.37704793, 0.45084634, 0.3079026]
64 | [0.33564404, 0.46575224, 0.33372045]
8 | [0.5397384, 0.41881782, 0.26093292]
66 | [0.42560518, 0.0136409905, 0.2709207]
26 | [0.37973955, 0.24594037, 0.61934566]
(10 rows)Upgrade the cluster
Up to now, we only support upgrading the server resource, plan and disk size. There are some restrictions on the upgrade operation, such as the cpu and memory of the server resource must be greater or equal to the original one, the disk size must be greater or equal to the original one. And the plan upgrade must from the Starter to Enterprise.
+ server_resource = "aws-r7i-large-2c-16g"
- server_resource = "aws-m7i-large-2c-8g"
+ pg_data_disk_size = "20"
- pg_data_disk_size = "10"$ terraform apply
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Refreshing state... [id=bbfb4ed2-b434-4e20-994f-6627e8f3785b]
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are
indicated with the following symbols:
~ update in-place
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster will be updated in-place
~ resource "pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster" "enterprise_plan_cluster" {
~ connect_endpoint = "postgres://test_user:q7SdfHYVqkGB@enterprise-plan-cluster-tiqmlrllv36fmh4h.eu-west-1-dev.aws.pgvecto.rs:5432/test?sslmode=require" -> (known after apply)
~ first_recoverability_point = "2024-09-20T03:53:04Z" -> (known after apply)
id = "bbfb4ed2-b434-4e20-994f-6627e8f3785b"
~ last_archived_wal_time = "2024-09-20T03:53:07Z" -> (known after apply)
~ last_updated = "2024-09-20T03:52:38Z" -> (known after apply)
~ pg_data_disk_size = "10" -> "20"
~ server_resource = "aws-m7i-large-2c-8g" -> "aws-r7i-large-2c-16g"
~ status = "Ready" -> (known after apply)
# (7 unchanged attributes hidden)
}
Plan: 0 to add, 1 to change, 0 to destroy.
Changes to Outputs:
~ psql_endpoint_enterprise = "postgres://test_user:q7SdfHYVqkGB@enterprise-plan-cluster-tiqmlrllv36fmh4h.eu-west-1-dev.aws.pgvecto.rs:5432/test?sslmode=require" -> (known after apply)
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Modifying... [id=bbfb4ed2-b434-4e20-994f-6627e8f3785b]
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Still modifying... [id=bbfb4ed2-b434-4e20-994f-6627e8f3785b, 10s elapsed]
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Still modifying... [id=bbfb4ed2-b434-4e20-994f-6627e8f3785b, 20s elapsed]
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Still modifying... [id=bbfb4ed2-b434-4e20-994f-6627e8f3785b, 30s elapsed]
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Still modifying... [id=bbfb4ed2-b434-4e20-994f-6627e8f3785b, 40s elapsed]
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Still modifying... [id=bbfb4ed2-b434-4e20-994f-6627e8f3785b, 50s elapsed]
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Modifications complete after 53s [id=bbfb4ed2-b434-4e20-994f-6627e8f3785b]
Apply complete! Resources: 0 added, 1 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
psql_endpoint_enterprise = "postgres://test_user:q7SdfHYVqkGB@enterprise-plan-cluster-tiqmlrllv36fmh4h.eu-west-1-dev.aws.pgvecto.rs:5432/test?sslmode=require"Destroy the cluster
$ terraform destroy
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Refreshing state... [id=bbfb4ed2-b434-4e20-994f-6627e8f3785b]
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are
indicated with the following symbols:
- destroy
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster will be destroyed
- resource "pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster" "enterprise_plan_cluster" {
- account_id = "8364ded2-5580-45c4-a394-edfa582e35a0" -> null
- cluster_name = "enterprise-plan-cluster" -> null
- cluster_provider = "aws" -> null
- connect_endpoint = "postgres://test_user:q7SdfHYVqkGB@enterprise-plan-cluster-tiqmlrllv36fmh4h.eu-west-1-dev.aws.pgvecto.rs:5432/test?sslmode=require" -> null
- database_name = "test" -> null
- first_recoverability_point = "2024-09-20T03:53:04Z" -> null
- id = "bbfb4ed2-b434-4e20-994f-6627e8f3785b" -> null
- image = "15-v0.3.0-public" -> null
- last_archived_wal_time = "2024-09-20T03:53:07Z" -> null
- last_updated = "2024-09-20T03:55:04Z" -> null
- pg_data_disk_size = "20" -> null
- plan = "Enterprise" -> null
- region = "eu-west-1" -> null
- server_resource = "aws-r7i-large-2c-16g" -> null
- status = "Ready" -> null
}
Plan: 0 to add, 0 to change, 1 to destroy.
Changes to Outputs:
- psql_endpoint_enterprise = "postgres://test_user:q7SdfHYVqkGB@enterprise-plan-cluster-tiqmlrllv36fmh4h.eu-west-1-dev.aws.pgvecto.rs:5432/test?sslmode=require" -> null
Do you really want to destroy all resources?
Terraform will destroy all your managed infrastructure, as shown above.
There is no undo. Only 'yes' will be accepted to confirm.
Enter a value: yes
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Destroying... [id=bbfb4ed2-b434-4e20-994f-6627e8f3785b]
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Destruction complete after 1s
Destroy complete! Resources: 1 destroyed.5. Recovery
In this section, we will show you how to restore your PostgreSQL database from existing backup or point-in-time recovery (PITR).
Recovery from the backup
WARNING
The cluster you are restoring to should have the same image,database name and region as the backup.
Get the backup id from dashboard
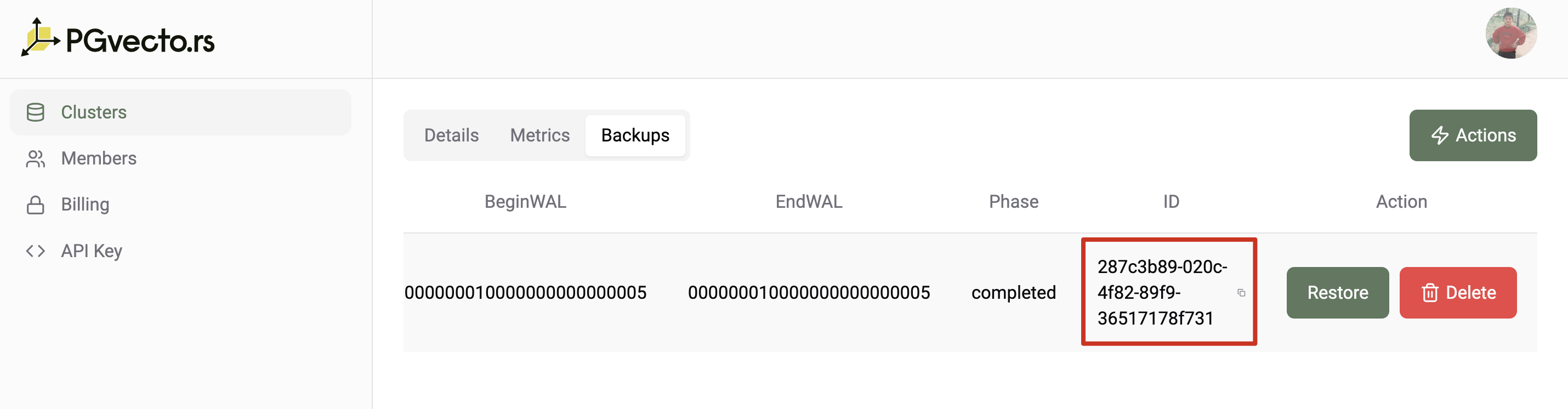
Create a new cluster with the backup id
terraform {
required_providers {
pgvecto-rs-cloud = {
source = "tensorchord/pgvecto-rs-cloud"
}
}
}
provider "pgvecto-rs-cloud" {
api_key = "pgrs-57cc0d484e7e1d00444201ee846455b5"
api_url = "https://cloud-dev.pgvecto.rs/api/v1"
}
resource "pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster" "enterprise_plan_cluster" {
account_id = "8364ded2-5580-45c4-a394-edfa582e35a0"
cluster_name = "enterprise-plan-cluster"
plan = "Enterprise"
image = "15-v0.3.0-public"
server_resource = "aws-r7i-large-2c-16g"
region = "eu-west-1"
cluster_provider = "aws"
database_name = "test"
pg_data_disk_size = "20"
enable_restore = "true"
backup_id = "4f53b451-8e19-443c-bcd7-43420d105696"
}
output "psql_endpoint_enterprise" {
description = "Endpoint for the PGVecto.rs Cloud Enterprise PostgreSQL database"
value = pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster.connect_endpoint
}$ terraform apply
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are
indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster will be created
+ resource "pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster" "enterprise_plan_cluster" {
+ account_id = "8364ded2-5580-45c4-a394-edfa582e35a0"
+ backup_id = "4f53b451-8e19-443c-bcd7-43420d105696"
+ cluster_name = "enterprise-plan-cluster"
+ cluster_provider = "aws"
+ connect_endpoint = (known after apply)
+ database_name = "test"
+ enable_restore = true
+ first_recoverability_point = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ image = "15-v0.3.0-public"
+ last_archived_wal_time = (known after apply)
+ last_updated = (known after apply)
+ pg_data_disk_size = "20"
+ plan = "Enterprise"
+ region = "us-east-1"
+ server_resource = "aws-r7i-large-2c-16g"
+ status = (known after apply)
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Changes to Outputs:
+ psql_endpoint_enterprise = (known after apply)
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Creating...
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Still creating... [10s elapsed]
...[snip]...
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Still creating... [2m10s elapsed]
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Creation complete after 2m19s [id=8ba9e5b4-f06c-4ef0-8e10-b6663237a532]
Apply complete! Resources: 1 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
psql_endpoint_enterprise = "postgres://test_user:j4Xu6TIstD1F@enterprise-plan-cluster-kxy2lovbc4crarmn.modelz.tech:5432/test?sslmode=require"# you can check the table and index
$ psql "postgres://test_user:j4Xu6TIstD1F@enterprise-plan-cluster-kxy2lovbc4crarmn.modelz.tech:5432/test?sslmode=require"
psql (15.3, server 15.8 (Debian 15.8-1.pgdg120+1))
SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, compression: off)
Type "help" for help.
test=> \dt
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------+-------+-----------
public | test | table | test_user
(1 row)
test=> SELECT * FROM test ORDER BY embedding <-> '[0.40671515, 0.24202824, 0.37059402]' LIMIT 10;
id | embedding
----+--------------------------------------
34 | [0.4047166, 0.2152912, 0.30516902]
56 | [0.39068437, 0.3153389, 0.40011033]
42 | [0.43917453, 0.22915891, 0.44726416]
45 | [0.47589824, 0.33998397, 0.39237767]
43 | [0.46702152, 0.09506769, 0.4343289]
95 | [0.4987348, 0.08346876, 0.28716254]
60 | [0.5421089, 0.3585022, 0.25259662]
80 | [0.61970145, 0.2186208, 0.36950335]
53 | [0.3399207, 0.3417044, 0.55435336]
54 | [0.3198571, 0.445044, 0.36041933]
(10 rows)PITR
WARNING
The cluster you are restoring to should have the same image,database name as the cluster.
Get cluster id from dashboard

Create a new cluster with the cluster id and target time
terraform {
required_providers {
pgvecto-rs-cloud = {
source = "tensorchord/pgvecto-rs-cloud"
}
}
}
provider "pgvecto-rs-cloud" {
api_key = "pgrs-57cc0d484e7e1d00444201ee846455b5"
api_url = "https://cloud-dev.pgvecto.rs/api/v1"
}
resource "pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster" "enterprise_plan_cluster" {
account_id = "8364ded2-5580-45c4-a394-edfa582e35a0"
cluster_name = "enterprise-plan-cluster"
plan = "Enterprise"
image = "15-v0.3.0-public"
server_resource = "aws-r7i-large-2c-16g"
region = "eu-west-1"
cluster_provider = "aws"
database_name = "test"
pg_data_disk_size = "20"
enable_restore = "true"
target_cluster_id = "43f17a52-0d07-43d5-91b6-9fbe4641578c"
target_time = "2024-09-20T12:00:00+08:00"
}
output "psql_endpoint_enterprise" {
description = "Endpoint for the PGVecto.rs Cloud Enterprise PostgreSQL database"
value = pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster.connect_endpoint
}$ terraform apply
Terraform used the selected providers to generate the following execution plan. Resource actions are
indicated with the following symbols:
+ create
Terraform will perform the following actions:
# pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster will be created
+ resource "pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster" "enterprise_plan_cluster" {
+ account_id = "8364ded2-5580-45c4-a394-edfa582e35a0"
+ cluster_name = "enterprise-plan-cluster"
+ cluster_provider = "aws"
+ connect_endpoint = (known after apply)
+ database_name = "test"
+ enable_restore = true
+ first_recoverability_point = (known after apply)
+ id = (known after apply)
+ image = "15-v0.3.0-public"
+ last_archived_wal_time = (known after apply)
+ last_updated = (known after apply)
+ pg_data_disk_size = "20"
+ plan = "Enterprise"
+ region = "eu-west-1"
+ server_resource = "aws-r7i-large-2c-16g"
+ status = (known after apply)
+ target_cluster_id = "43f17a52-0d07-43d5-91b6-9fbe4641578c"
+ target_time = "2024-09-20T12:00:00+08:00"
}
Plan: 1 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
Changes to Outputs:
+ psql_endpoint_enterprise = (known after apply)
Do you want to perform these actions?
Terraform will perform the actions described above.
Only 'yes' will be accepted to approve.
Enter a value: yes
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Creating...
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Still creating... [10s elapsed]
...[snip]...
pgvecto-rs-cloud_cluster.enterprise_plan_cluster: Still creating... [5m20s elapsed]
# you can check the table and index
$ psql 'postgres://test_user:RKC4wr7MRcwm@enterprise-plan-cluster-4paxqvbzwxudmvja.eu-west-1-dev.aws.pgvecto.rs:5432/test?sslmode=require'
psql (15.3, server 15.8 (Debian 15.8-1.pgdg120+1))
SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, compression: off)
Type "help" for help.
test=> \dt
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+------+-------+-----------
public | test | table | test_user
(1 row)
test=> SELECT * FROM test ORDER BY embedding <-> '[0.40671515, 0.24202824, 0.37059402]' LIMIT 10;
id | embedding
----+--------------------------------------
34 | [0.4047166, 0.2152912, 0.30516902]
56 | [0.39068437, 0.3153389, 0.40011033]
42 | [0.43917453, 0.22915891, 0.44726416]
45 | [0.47589824, 0.33998397, 0.39237767]
43 | [0.46702152, 0.09506769, 0.4343289]
95 | [0.4987348, 0.08346876, 0.28716254]
60 | [0.5421089, 0.3585022, 0.25259662]
80 | [0.61970145, 0.2186208, 0.36950335]
53 | [0.3399207, 0.3417044, 0.55435336]
54 | [0.3198571, 0.445044, 0.36041933]
(10 rows)